quickgraph
Commandline tool to quickly make graphs from arbitrary text files
QuickGraph
A commandline tool to quickly make graphs from arbitrary text files.
Released under the Boost Software License (Version 1.0).
Note: I wouldn't use this just yet. It is probably littered with bugs and certainly incomplete ideas.
Syntax
Syntax: qg [options] logfile [... logfile]
Options:
-h,--help This help output
-v,--verbose Verbose mode
-o,--output FILENAME Output filename (default: quickgraph.html)
-a,--alias ALIAS Use named alias from your home directory's .quickgraphrc
-g,--graph Begin a new graph. This is not necessary if you're only making one
-t,--title TITLE Sets the title of the current graph
-x REGEX Matches a new X axis value, parsed by -e, formatted with -f or -F
-y REGEX Matches a new Y axis value, parsed by -e, formatted with -f or -F
-c,--color COLOR Sets the color for the current rule (only makes sense on Y axis rules)
-l,--legend LEGEND Sets the legend for the current axis
-e,--eval CODE Sets the evaluator for the axis regex's output. See examples
-f,--format CODE Sets the code used to format an x axis value
--consolidate FUNC Sets the consolidation function for the current axis (sum, count, avg, min, max, last)
--width Sets the graph's width. Defaults to use the whole width of the browser.
--height Sets the graph's height. Defaults to 480.
-A RESTOFLINE Create a new alias (like in quickgraphrc) statement; only works in a response file
Example 1
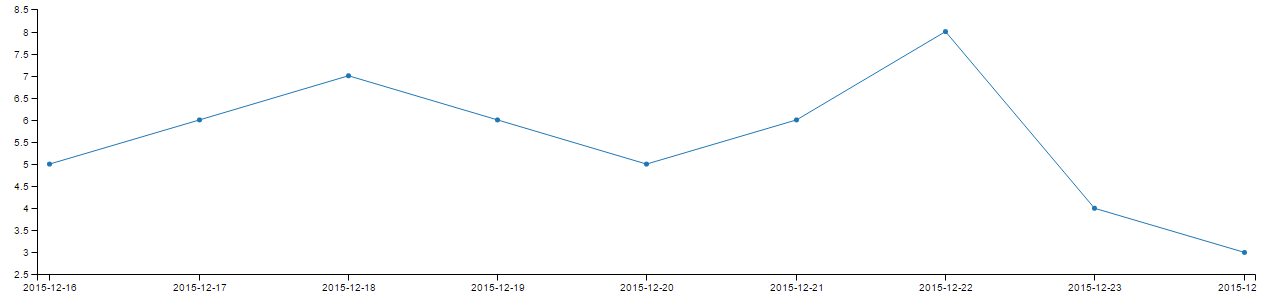
Data (example1.txt):
2015-12-16 5
2015-12-17 6
2015-12-18 7
2015-12-19 6
2015-12-20 5
2015-12-21 6
2015-12-22 8
2015-12-23 4
2015-12-24 3
Commandline:
qg example1.txt -x "^[-\d]+" -a date -y "\d+$"
Example 2
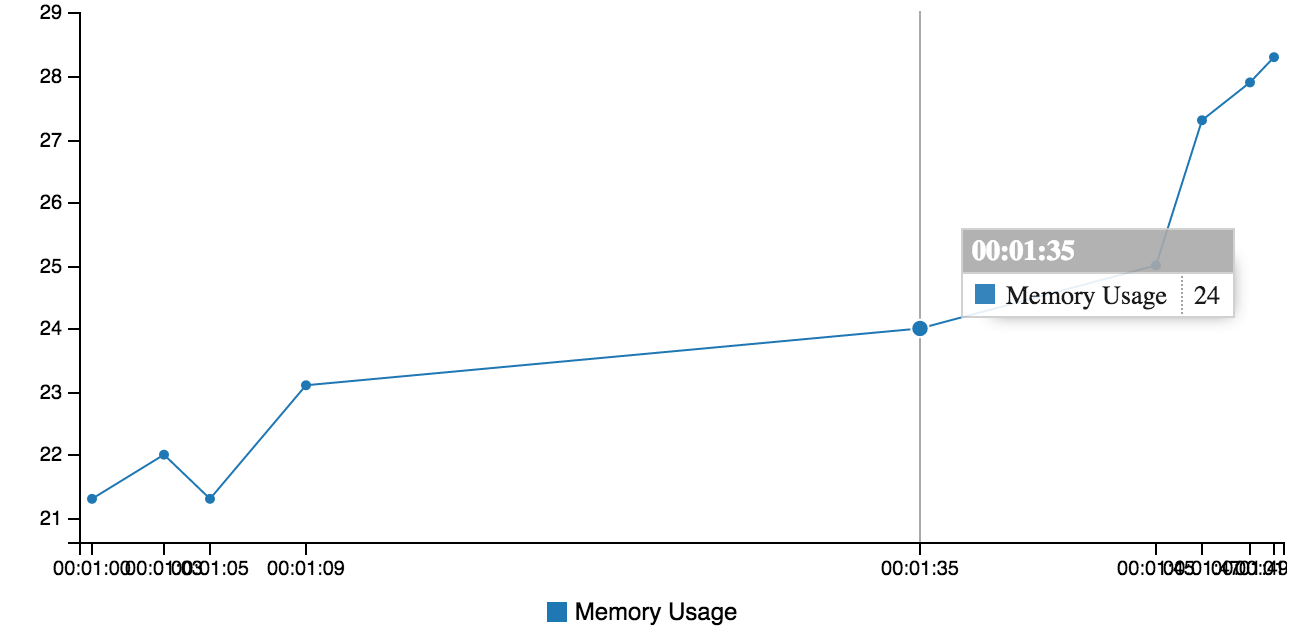
Data: (example2.txt)
00:01:00 memory usage 21.3mb
00:01:03 memory usage 22.0mb
00:01:05 memory usage 21.3mb
00:01:09 memory usage 23.1mb
00:01:35 memory usage 24mb
00:01:45 memory usage 25mb
00:01:47 memory usage 27.3mb
00:01:49 memory usage 27.9mb
00:01:50 memory usage 28.3mb
Commandline:
qg example2.txt -x "(?<H>\d\d):(?<M>\d\d):(?<S>\d\d)" -e "@f.H*3600+@f.M*60+@f.S" -y "memory usage ([\d\.]+)mb" -l "Memory Usage"